How to do Futures Trading on Gate.io

What are Perpetual Futures Contracts?
A futures contract is a legally binding agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. These assets can vary from commodities like gold or oil to financial instruments such as cryptocurrencies or stocks. This type of contract serves as a versatile tool for both hedging against potential losses and securing profits.
Perpetual futures contracts, a subtype of derivatives, enable traders to speculate on the future price of an underlying asset without actually owning it. Unlike regular futures contracts with set expiration dates, perpetual futures contracts do not expire. Traders can maintain their positions for as long as they desire, allowing them to capitalize on long-term market trends and potentially earn substantial profits. Additionally, perpetual futures contracts often feature unique elements like funding rates, which help align their price with the underlying asset.
One distinctive aspect of perpetual futures is the absence of settlement periods. Traders can keep a position open for as long as they have sufficient margin, without being bound by any contract expiry time. For instance, if you purchase a BTC/USDT perpetual contract at $30,000, there is no obligation to close the trade by a specific date. You have the flexibility to secure your profit or cut losses at your discretion. It’s worth noting that trading perpetual futures is not allowed in the U.S., although it constitutes a substantial portion of global cryptocurrency trading.
While perpetual futures contracts offer a valuable tool for gaining exposure to cryptocurrency markets, it’s essential to acknowledge the associated risks and exercise caution when engaging in such trading activities.
Explanation of Terminology on the Futures Trading Page on Gate.io
For beginners, futures trading can be more complex than spot trading, as it involves a greater number of professional terms. To help new users understand and master futures trading effectively, this article aims to explain the meanings of these terms as they appear on the Gate.io futures trading page.We will introduce these terms in order of appearance, starting from left to right.
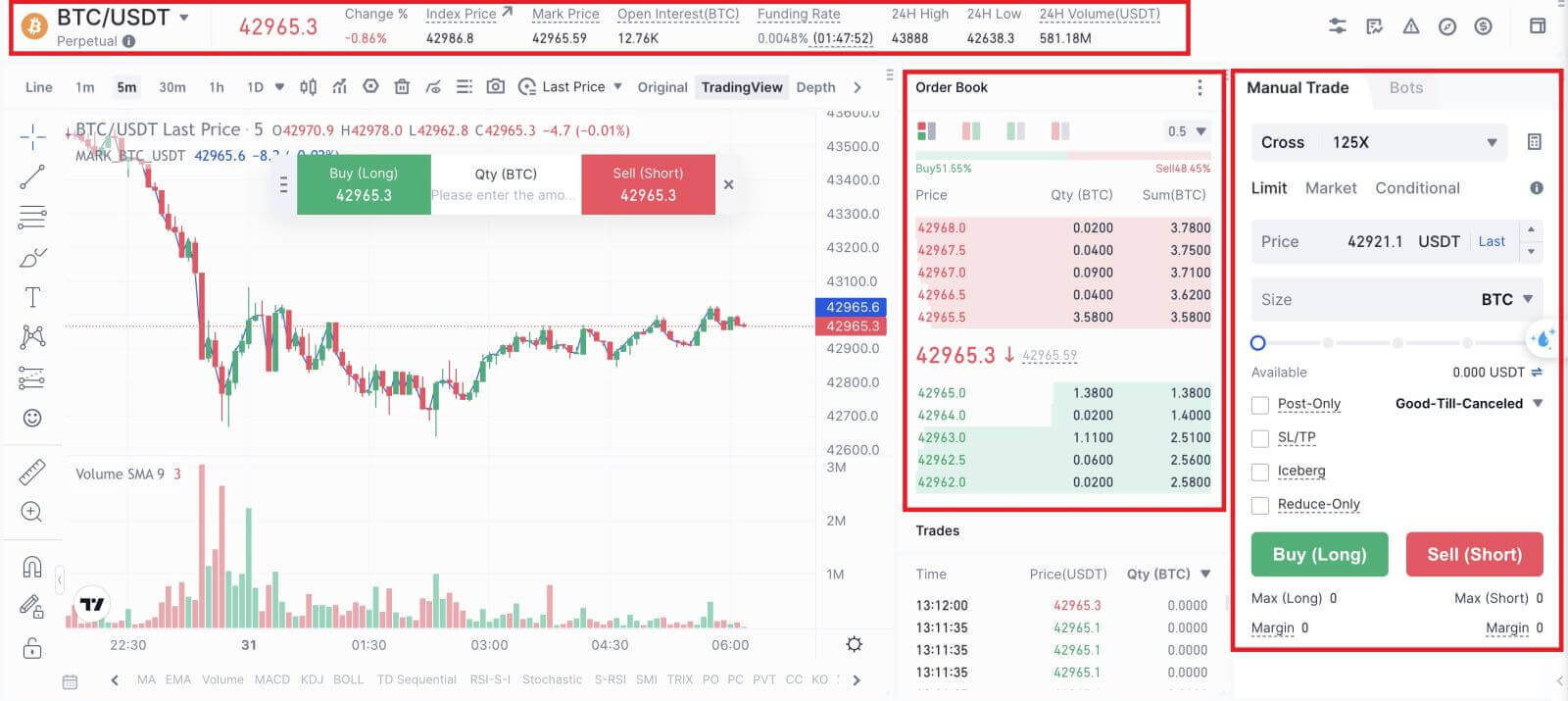
Terms above the K-line chart
Perpetual: "Perpetual" denotes continuity. The commonly seen "perpetual futures" (also known as perpetual futures contracts) evolved from traditional financial futures contracts, with the key difference being that perpetual futures have no settlement date. This means that as long as the position is not closed due to forced liquidation, it will remain open indefinitely.Index Price: The comprehensive price index obtained by referencing the prices of major mainstream exchanges and calculating the weighted average of their prices. The index price displayed on the current page is the BTC index price.
Mark Price: The real-time fair price of the futures, calculated based on the index price and market price. It is used to calculate the floating PNL of positions and determine position liquidation. It may deviate from the last price of the futures to avoid price manipulation.
Funding Rate: The funding rate in the current stage. If the rate is positive, long position holders pay the funding fee to short position holders. If the rate is negative, short position holders pay the funding fee to long position holders.

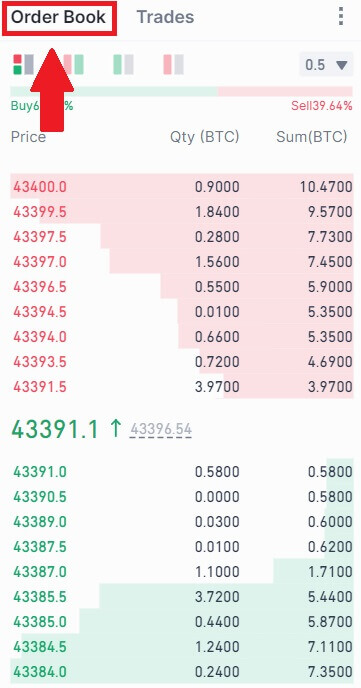
Terms in the order book area
Order Book: A window to observe market trends during the trading process. In the order book area, you can observe each trade, the proportion of buyers and sellers, and more.
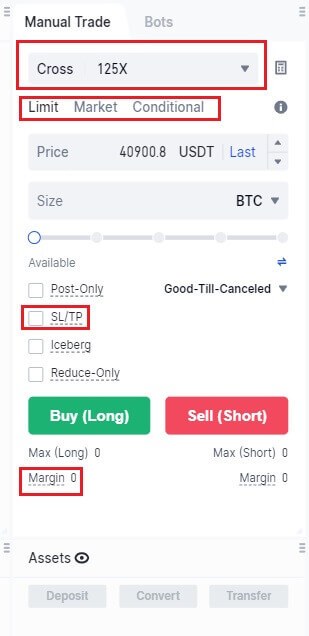
Terms in the trading area
Open Long: When you predict that the token price will rise in the future and open a position based on this trend, it is known as opening a long position.
Open Short: When you predict that the token price will fall in the future and open a position based on this trend, it is known as opening a short position.
Margin and Margin Mode: Users can engage in futures trading after depositing a certain percentage of funds as financial collateral. This fund is known as margin. The margin mode is divided into isolated margin or cross margin.
Isolated: In isolated margin mode, a certain amount of margin is allocated to a position. If the margin for a position decreases to a level below the maintenance margin, the position will be liquidated. You can also choose to add or reduce margin to this position.
Cross: In cross margin mode, all positions share the cross margin of the asset. In the event of liquidation, the trader may lose all the margin and all positions under the cross margin of that asset.
Order Types: The order types are divided into limit order, market order, trigger order, trailing stop order, and post-only order.
-
Limit: A limit order is an order placed to buy or sell at a specific price or better. However, a limit order’s execution isn’t guaranteed.
-
Market: A market order is an order placed to buy or sell quickly at the best available price in the market.
-
Trigger: For trigger orders, users can set a trigger price, order price, and quantity in advance. When the market price reaches the trigger price, the system will automatically place an order at the order price. Before the trigger order is triggered successfully, the position or margin will not be frozen.
-
Trailing Stop: A trailing stop order is submitted to the market based on the user’s settings as a strategic order when the market is in a retracement. Actual Trigger Price = Market’s Highest (Lowest) Price ± Trail Variance (Price Distance), or Market’s Highest (Lowest) Price * (1 ± Trail Variance). At the same time, users can set the price at which the order is activated before the trigger price is calculated.
-
Post Only: A post-only order will not be immediately executed in the market, ensuring that the user will always be the maker. If the order were to be matched with an existing order immediately, it would be canceled.
-
SL/TP: A SL/TP order is an order with preset trigger conditions (take profit price or stop-loss price). When the last price / fair price / index price reaches the preset trigger price, the system will close the position at the best market price, based on the preset trigger price and quantity. This is done to achieve the goal of taking profit or stopping losses, allowing users to automatically settle the desired profit or avoid unnecessary losses.
-
Stop Limit Order: A stop limit order is a preset order where users can set the stop-loss price, limit price, and buy/sell amount in advance. When the last price reaches the stop-loss price, the system will automatically place an order at the limit price.
-
COIN-M: Coin-margined futures provided by Gate.io are a reverse contract that uses cryptocurrency as collateral, meaning that cryptocurrency serves as the base currency. For example, in the case of BTC coin-margined futures, Bitcoin is used as the initial margin and for PNL calculations.
-
USDT-M: USDT-margined futures provided by Gate.io is a linear contract, which is a linear derivative product quoted and settled in USDT, a stablecoin pegged to the value of the US dollar.
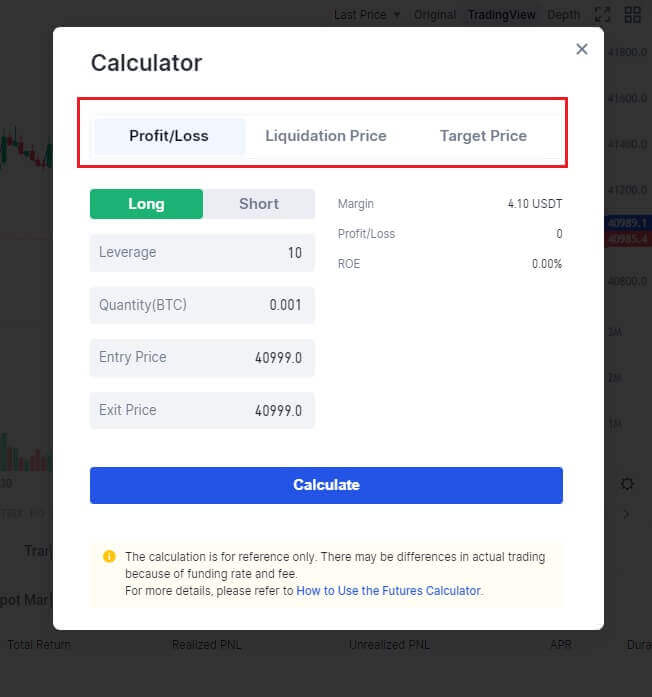
Terms in the Futures Calculator Area
PNL: Enter your entry price, the quantity of futures you hold, and the leverage multiplier. Then, set your expected close price to calculate the final earnings and yield.
Liquidation Price: Enter your entry price, the quantity of futures you hold, and the leverage multiplier. Then, select the margin mode (cross or isolated) to calculate your liquidation price.
Target Price: Enter your entry price, the quantity of futures you hold, and the leverage multiplier. Then, set your desired yield to calculate the final earnings and yield.
Note: The results calculated using the futures calculator are for reference purposes only, and the actual results in live trading will prevail.
Terms in the order area below the K-line chart
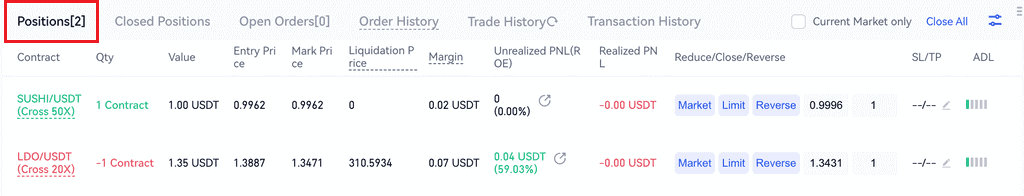
1. Position Tab: This shows all positions you are holding, including:
- Contract: Your contract holding.
- Qty: This shows the quantity of contracts you have ordered, a positive number indicates a long position, and a negative number indicates a short position. You can switch the quantity unit to contracts or currency in the order zone.
- Value: This refers to the position value at the mark price.
- Entry Price: This refers to the average price of buying a long position or selling a short position.
- Mark Price: Mark price tends to be the fair price of the contract, which is calculated based on underlying asset’s spot index price and a decaying funding rate basis rate
- Liquidation Price: This shows the liquidation price of your position. The closer the mark price is to the liquidation price, the higher the risk that the current position will be liquidated, and vice versa, the lower the risk that the position will be liquidated. Please note that Gate.io uses mark price to trigger liquidation. When mark price reaches the liquidation price, the liquidation will be triggered.
- Margin:This refers to the principle that you need when opening a position in futures trading.
- Unrealized PNL (ROE): Unrealized PNL shows the real-time unrealized profit or loss of the open position
- Realized PNL: Realized PNL refers to the actual profit and loss after exiting a position, calculated based on the entry and exit prices
-
Reduce/ Close/ Reverse Positions:
Reduce Positions: It refers to closing part of orders, and it is generally used to stop profit.
Close Positions: You can choose market order or limit order to close the position, the order is filled when it is closed.
Reverse Positions: After closing the original positions at the market price, submitting an order in the opposite side.
- ADL: You can set your take profit (TP) and stop loss (SL) orders in the position tab. Gate.io supports two SL/TP modes, which are position SL/TP and trigger SL/TP.
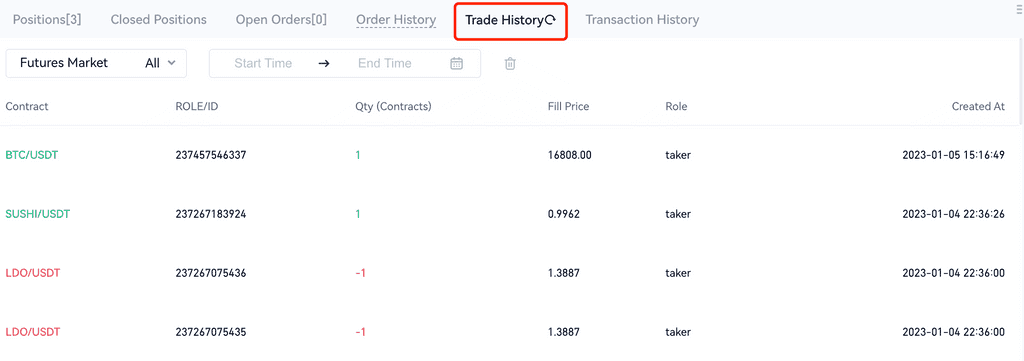
2. Order History: It includes the orders which are canceled, fully filled and partially filled. You can view detailed information here about the end time, side, order price, quantity, fill price, close reason and source.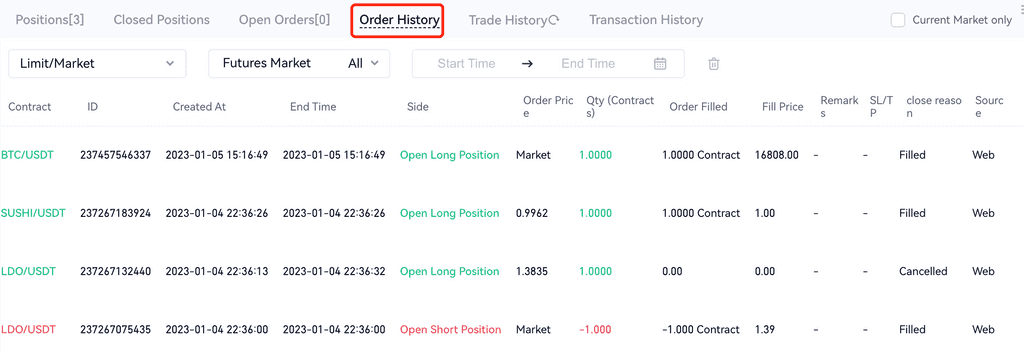
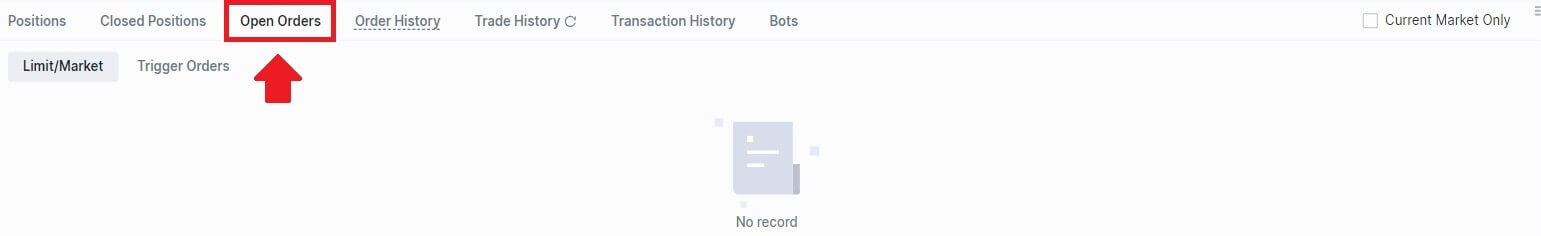
3. Open Orders: show all the pending orders.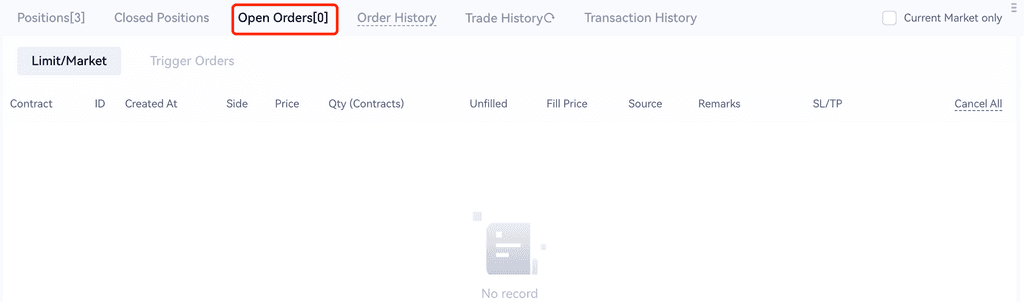
How to Trade USDT-M Perpetual Futures on Gate.io (Website)
1. Go to Gate.io Website, click on [Derivatives], select [USDT-M] on Perpetual Futures Section.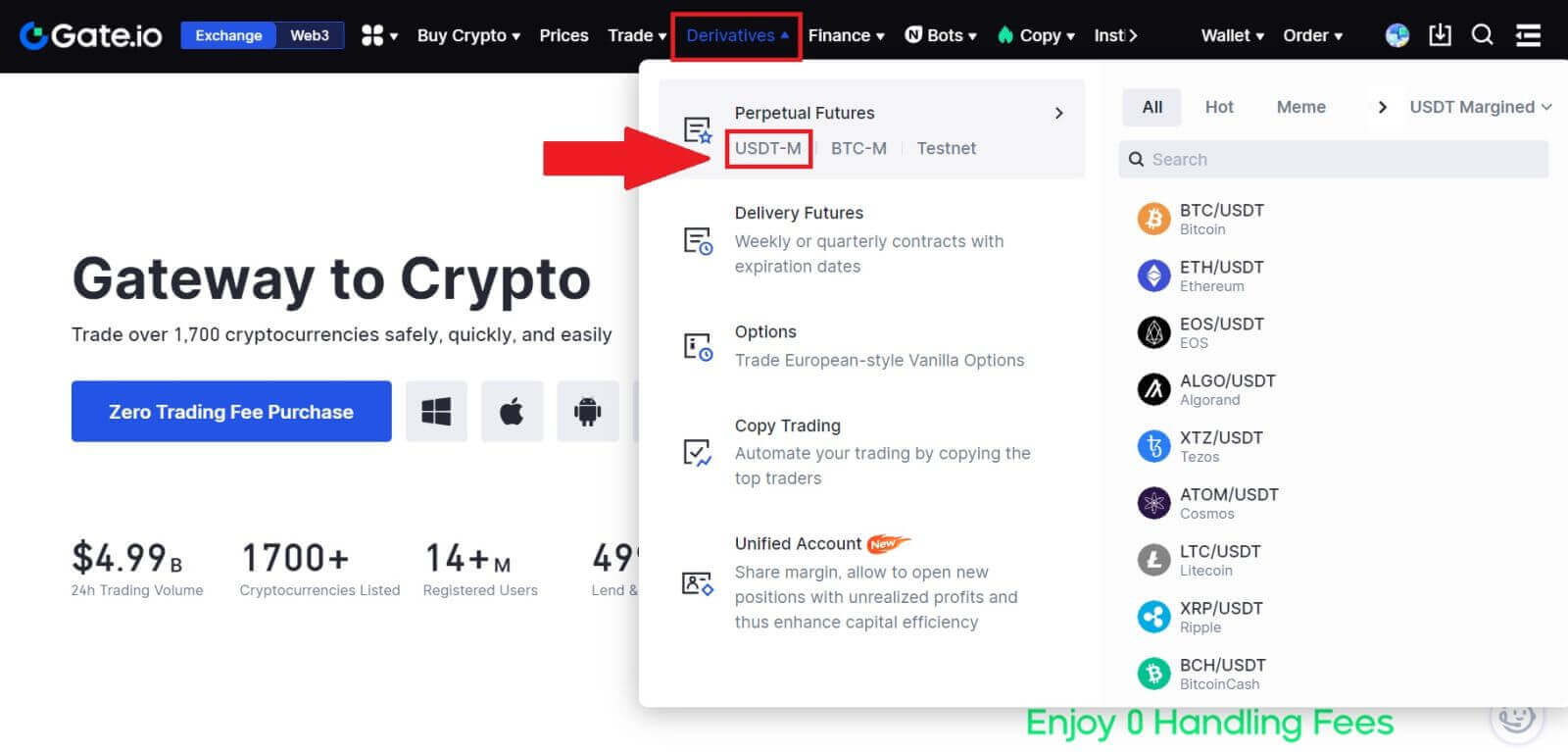
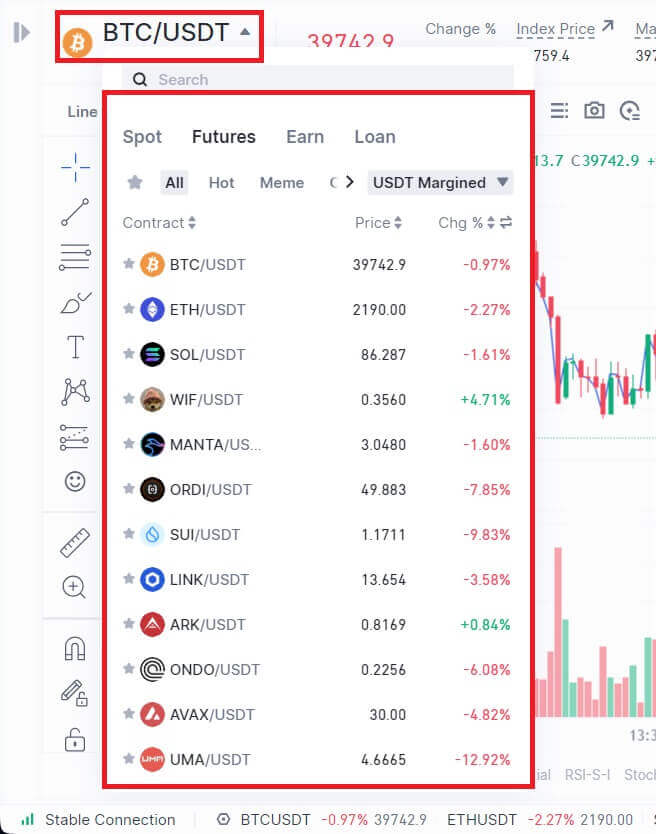
2. On the left-hand side, select BTC/USDT as an example from the list of futures.
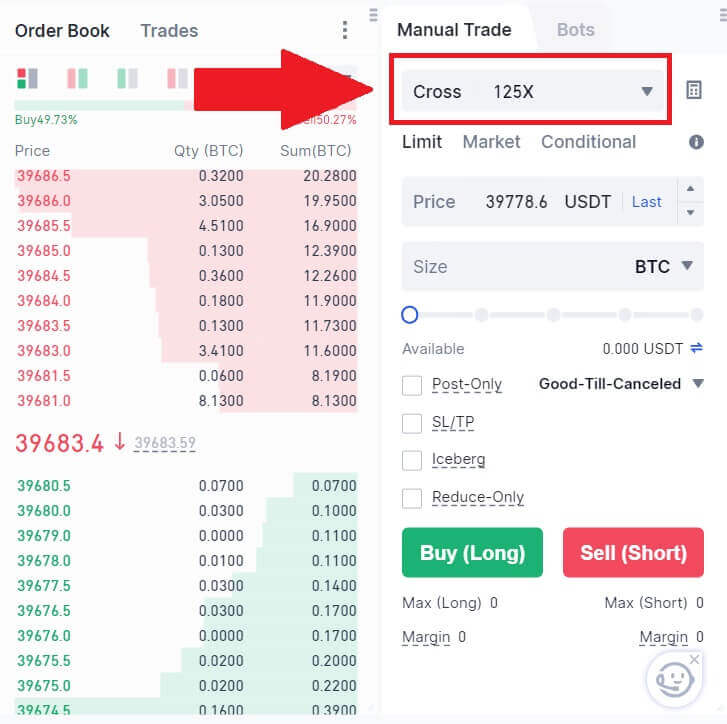
3. Click on the following part. Here, you can click on Isolated or Cross to choose your [Margin Mode].
Adjust the leverage multiplier by clicking on the number. After that, click [Confirm] to save your change.
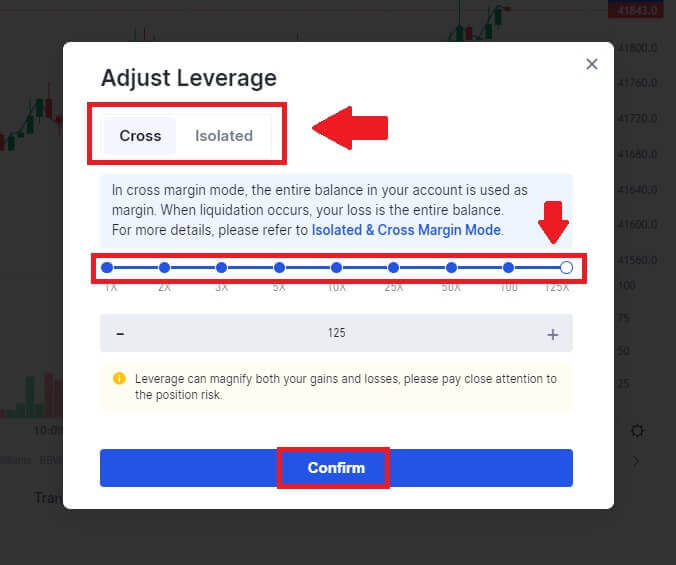
The platform supports traders with different margin preferences by offering different margin modes.
- The cross-margin mode shares margins with two positions opened against the same cryptocurrency. Any profit or loss from a position can be used to adjust against the balance of the other trade.
- The isolated margin only accepts margin against a position opened. In the event of a loss, the trade will only lose against the specific position on settlement. This leaves the balance of cryptocurrency untouched. This is the best option for all new traders since it protects the main crypto coin balance.
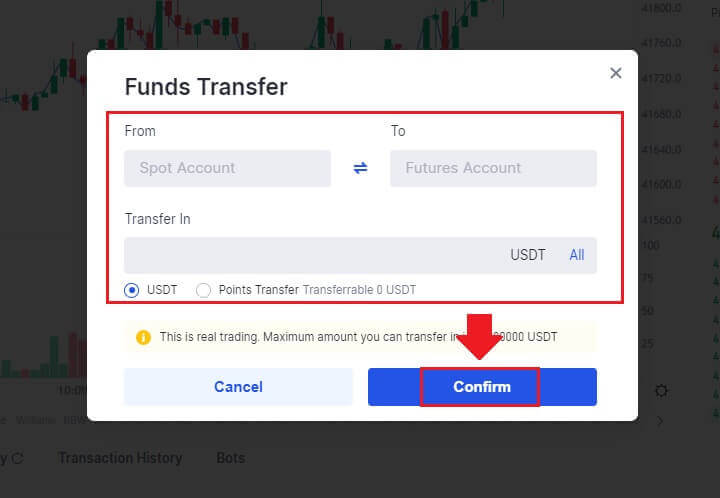
Once in the transfer menu, enter the desired amount you wish to transfer, and click on [Confirm].
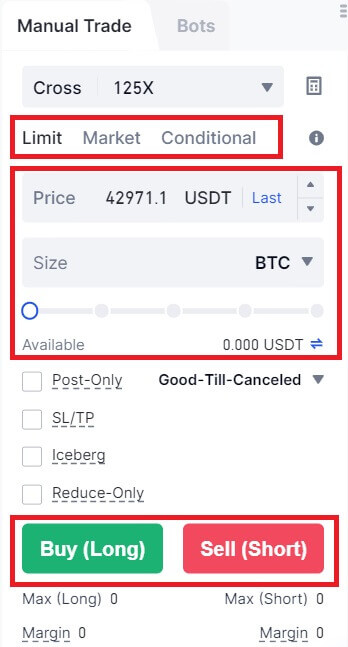
5. To open a position, users have three options: Limit Order, Market Order, and Trigger Order. Follow these steps:
Limit Order:
- Set your preferred buying or selling price.
- The order will only execute when the market price reaches the specified level.
- If the market price doesn’t reach the set price, the limit order remains in the order book, awaiting execution.
- This option involves a transaction without specifying a buying or selling price.
- The system executes the transaction based on the latest market price when the order is placed.
- Users only need to input the desired order amount.
Conditional Order:
- Set a trigger price, order price, and order quantity.
- The order will only be placed as a limit order with the predetermined price and quantity when the latest market price hits the trigger price.
- This type of order provides users with more control over their trades and helps automate the process based on market conditions.
6. After placing your order, view it under [Open Orders] at the bottom of the page. You can cancel orders before they’re filled.
How to Trade USDT-M Perpetual Futures on Gate.io (App)
1. Open your Gate.io App, on the first page, tap on [Futures] and choose [USDT-Perp].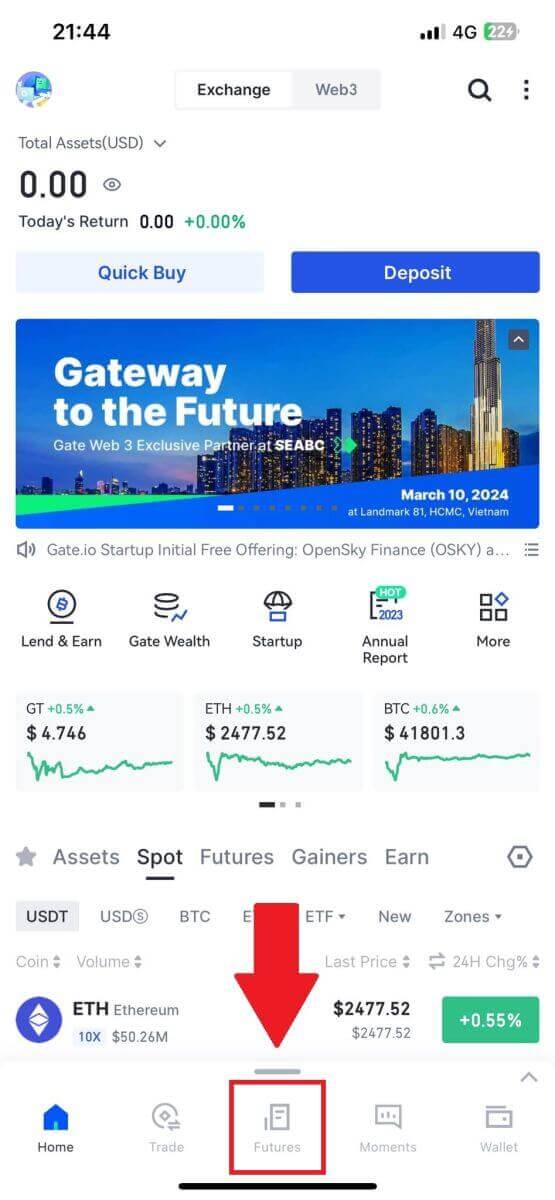
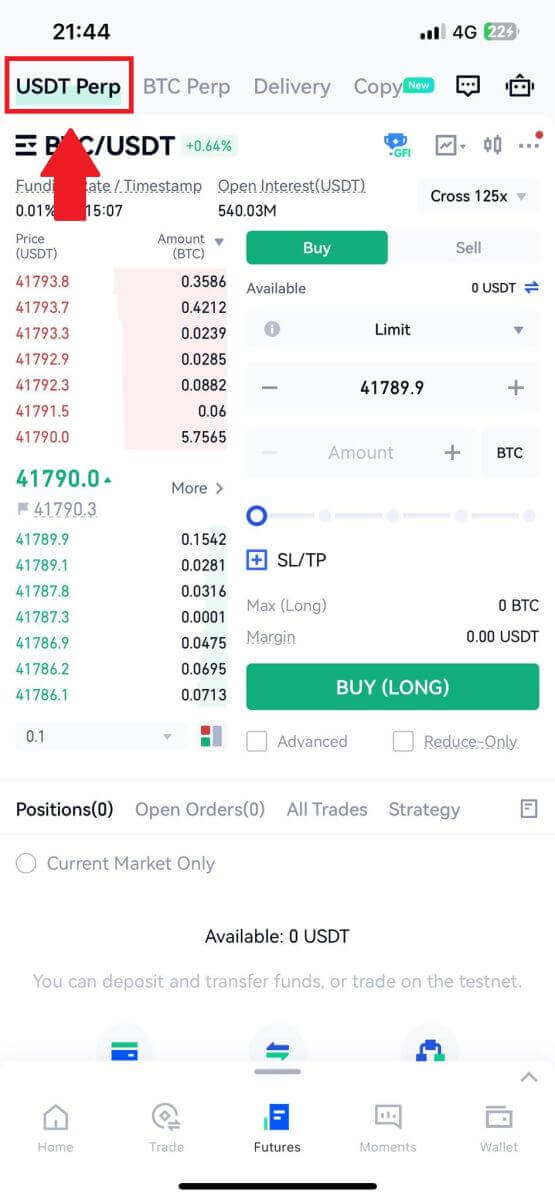
2. To switch between different trading pairs, tap on [BTC/USDT] located at the top left. You can then utilize the search bar for a specific pair or directly select from the listed options to find the desired futures for trading.
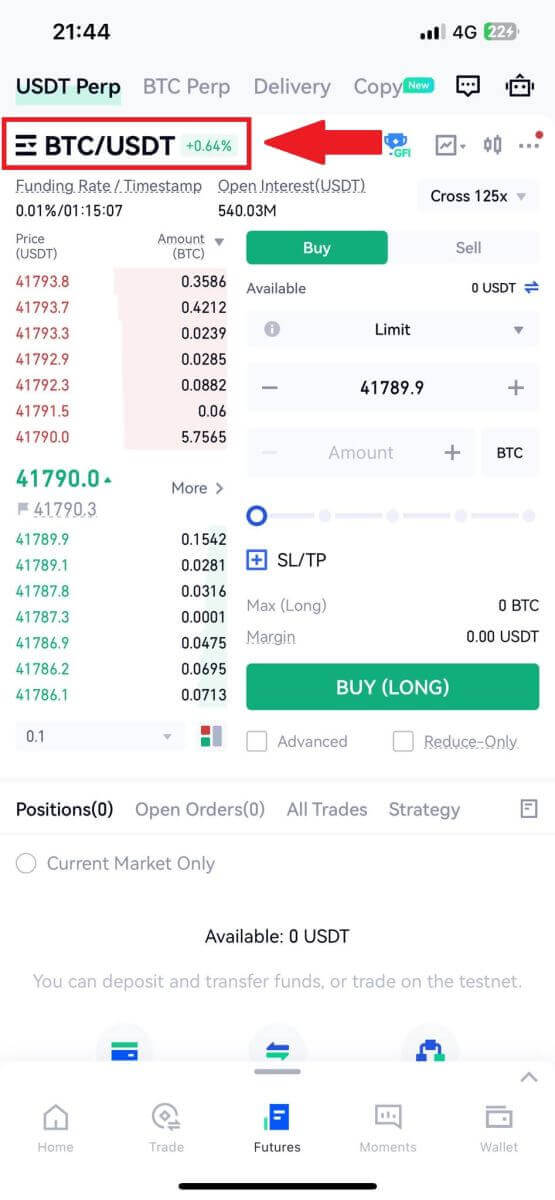
3. Choose the margin mode and adjust the leverage settings according to your preference, and tap [Confirm] to save the changes.
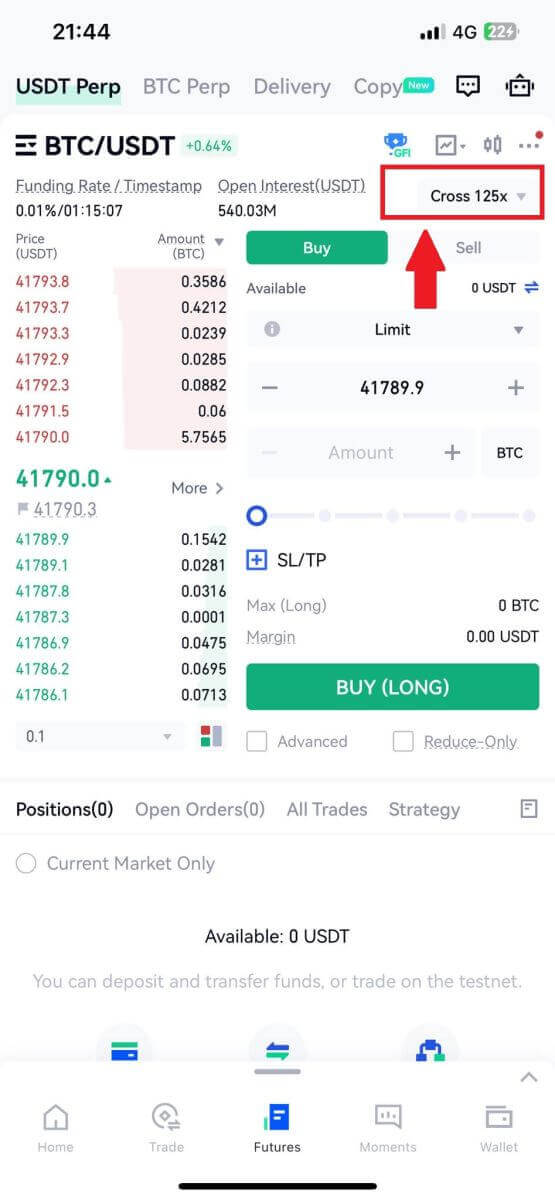
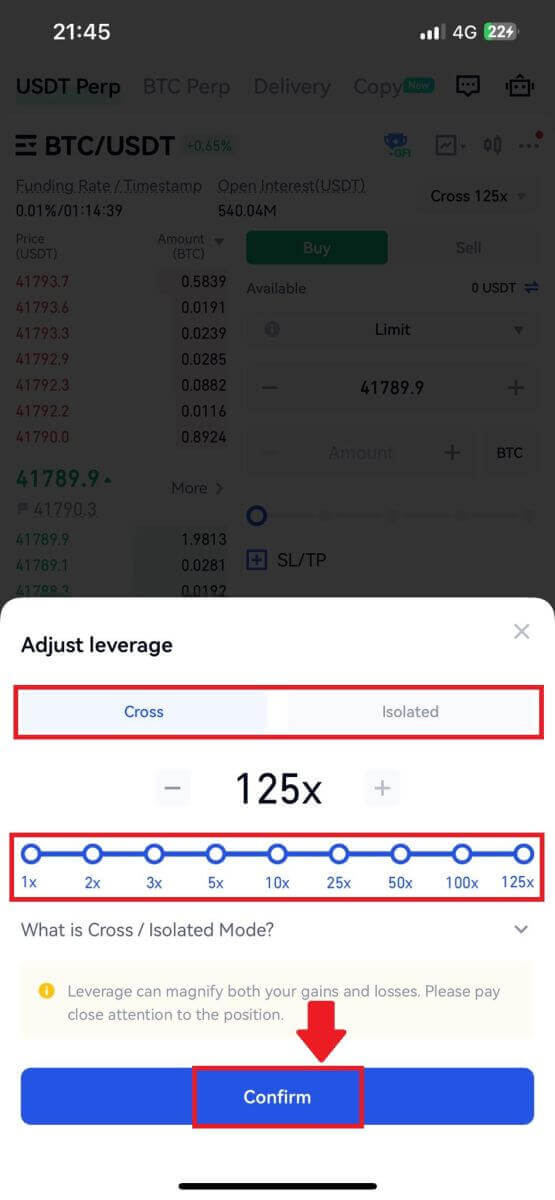
4. Choose your order type by tapping on the following.
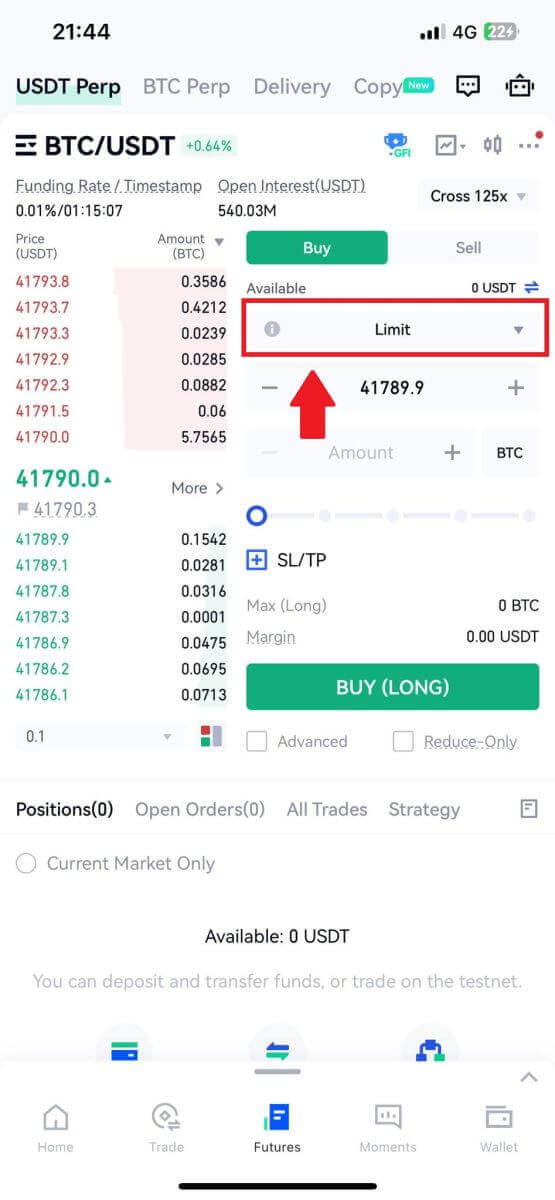
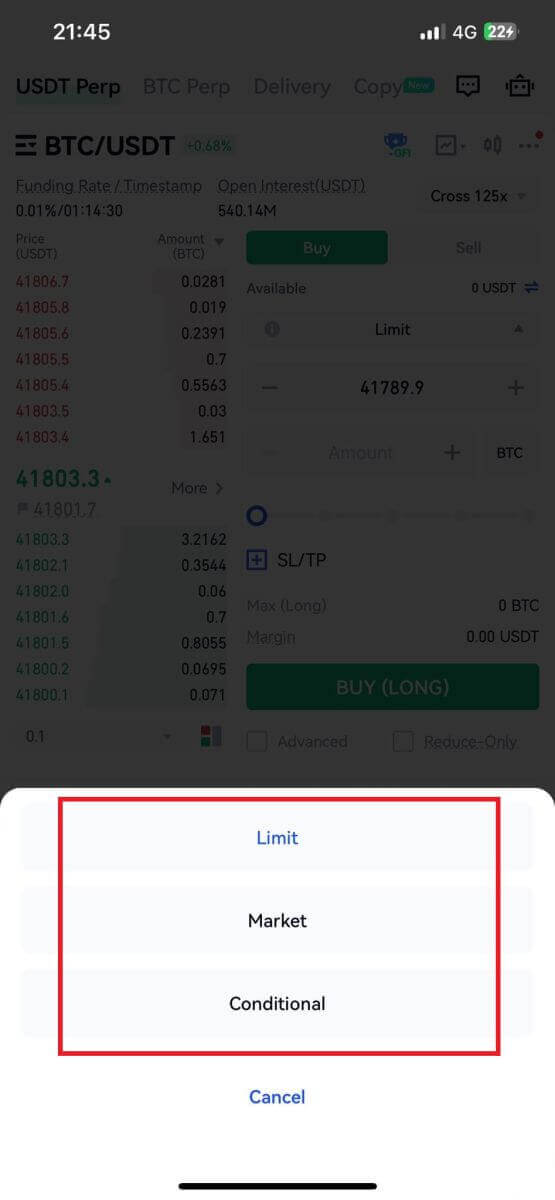
4. On the right side of the screen, place your order. For a limit order, enter the price and amount; for a market order, input only the amount. Tap [Buy (Long)] to initiate a long position, or [Sell (Short)] for a short position.
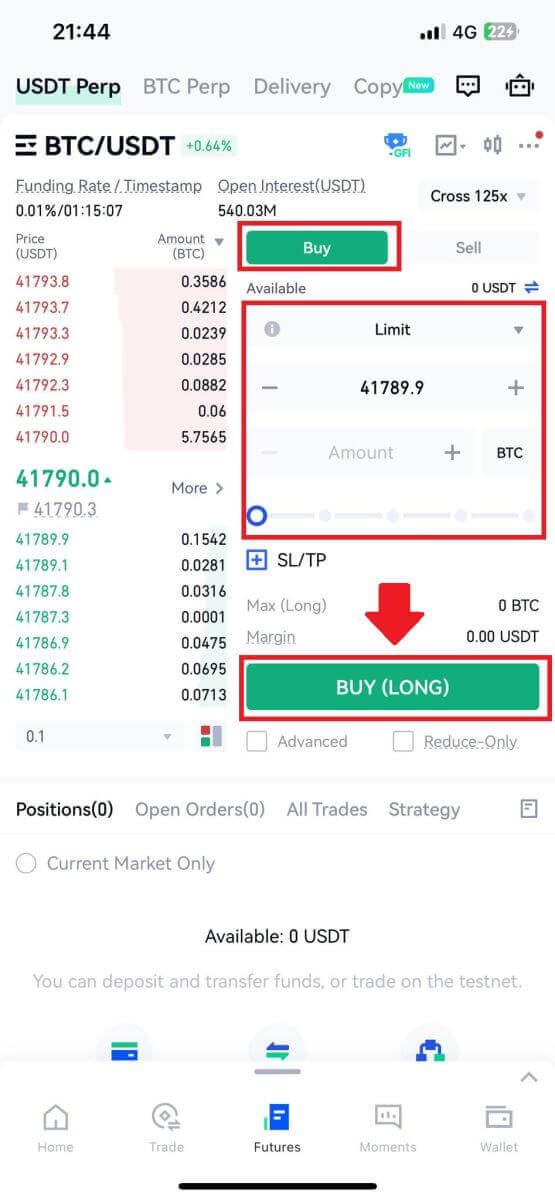
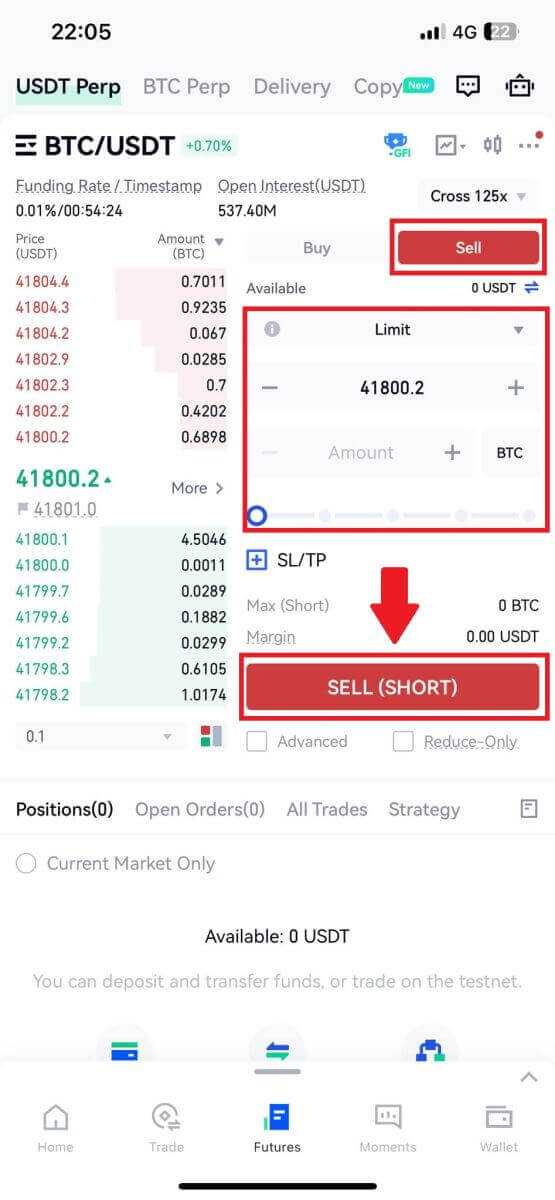
5. Once the order is placed, if it isn’t filled immediately, it will appear in [Open Orders].
Gate.io Future Trading Modes
Position Mode
(1) Hedge Mode
-
In Hedge Mode, users are required to explicitly indicate whether they intend to open or close a position when placing an order. This mode allows users to hold positions simultaneously in both long and short directions within the same futures contract. The leverages for the long and short positions are independent of each other.
-
All long positions are aggregated, and all short positions are combined within each futures contract. When maintaining positions in both long and short directions, the positions must allocate the corresponding margin based on the specified risk limit level.
For instance, in BTCUSDT futures, users have the flexibility to open a long position with 200x leverage and a short position with 200x leverage concurrently.
(2) One-Way Mode
In One-Way Mode, users are not required to specify whether they are opening or closing a position when placing an order. Instead, they only need to specify whether they are buying or selling. Additionally, users can only maintain positions in a single direction within each futures contract at any given time. If holding a long position, a sell order will automatically close it once filled. Conversely, if the number of filled sell orders surpasses the number of long positions, a short position will be initiated in the opposite direction.
Margin Modes
(1) Isolated Margin Mode
-
In Isolated Margin Mode, the potential loss of a position is limited to the initial margin and any additional position margin used specifically for that isolated position. In the event of liquidation, the user will only incur losses equivalent to the margin associated with the isolated position. The available balance of the account remains untouched and is not utilized as additional margin. Isolating the margin used in a position allows users to restrict losses to the initial margin amount, which can be beneficial in cases where a short-term speculative trading strategy doesn’t pan out.
-
Users can manually inject additional margin into isolated positions to optimize the liquidation price.
(2) Cross-Margin Mode
Cross Margin Mode involves using the entire available balance of the account as margin to secure all cross positions and prevent liquidation. In this margin mode, if the net asset value falls short of meeting the maintenance margin requirement, liquidation will be triggered. If a cross position undergoes liquidation, the user will lose all assets in the account except for the margin associated with other isolated positions.
Modifying Leverage
- Hedge mode allows users to employ different leverage multipliers for positions in the long and short directions.
- Leverage multipliers can be adjusted within the permitted range of the futures leverage multiplier.
- Hedge mode also permits the switching of margin modes, such as transitioning from isolated mode to cross margin mode.
- Note: If a user has a position in cross margin mode, it cannot be switched to isolated margin mode.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Types of Order on Gate.io Futures
Limit Order
Limit orders allow the trader to set a specific buying or selling price, and the order will be filled at the order price or at a price more favorable than the order price.
When a limit order is submitted, if there is no order of which price is more favorable than or equal to the order price available for matching in the order book, the limit order will enter the order book to be filled, increasing the market depth. After the order is filled, the trader will be charged according to the more favorable maker fee.
When a limit order is submitted, if an order of which price is more favorable than or equal to the order price is already available for matching in the order book, the limit order will be immediately filled at the current best available price. Because of the liquidity consumed during the order execution, a certain trading fee will be charged as the Taker fee expense.
In addition, limit orders can also be used to partially or fully close a take profit limit order. The advantage of a limit order is that it is guaranteed to be filled at the specified price, but there also exists a risk that the order will not be filled.
When using a limit order, the user can also switch the effective time type of the order according to their trading needs, and the default is GTC:
- GTC (Good ‘Til Canceled Order): This type of order will remain valid until it is fully filled or canceled.
- IOC (Immediate or Cancel Order): If this type of order cannot be filled immediately at the specified price, the unfilled part will be canceled.
- FOK (Fill or Kill Order): This type of order will be canceled immediately if all orders cannot be filled.
Market Order
The market order will be filled at the best price available in the order book at the time. The order can be quickly filled without having the trader set the price. The market order guarantees the execution of
orders but not the execution price, as it may fluctuate depending on market conditions. Market orders are typically used when a trader needs to make a quick entry to capture a market trend.
Conditional Order
If the trigger price is set, when the benchmark price (market price, index price, fair price) selected by the user reaches the trigger price, it will be triggered, and a limit order will be placed at the order price and quantity set by the user.
Post Only
Post-only orders will not be filled in the market immediately, which ensures that the user is always a maker and enjoys the yield of the trading fee as a liquidity provider; at the same time, if the order is filled with an existing order, then the order will be canceled immediately.
SL/TP
SL/TP refers to the pre-set trigger price (take profit price or stop loss price) and trigger price type. When the last price of the specified trigger price type reaches the pre-set trigger price, the system will place a close market order according to the pre-set quantity in order to take profit or stop loss. Currently, there are two ways to place a stop loss order:
- Set TP/SL when opening a position: This means to set TP/SL in advance for a position that is about to be opened. When the user places an order to open a position, they can click to set a TP/SL order at the same time. When the open position order is filled (partially or fully), the system will immediately place a TP/SL order with the trigger price and trigger price type pre-set by the user. (This can be viewed in open orders under TP/SL.)
- Set TP/SL when holding a position: Users can set a TP/SL order for a specified position when holding a position. After the setting is complete, when the last price of the specified trigger price type meets the trigger condition, the system will place a close market order according to the quantity set in advance.
Differences between Coin-M Perpetual Futures and USDT-M Perpetual Futures
1. Different crypto is used as the valuation unit, collateral asset, and calculation of PNL:
- In USDT-M perpetual futures, valuation and pricing are in USDT, with USDT also used as collateral, and PNL calculated in USDT. Users can engage in diverse futures trading by holding USDT.
- For Coin-M perpetual futures, pricing and valuation are in US dollars (USD), utilizing the underlying cryptocurrency as collateral, and calculating PNL with the underlying crypto. Users can participate in specific futures trading by holding the corresponding underlying crypto.
2. Different contract values:
- The value of each contract in USDT-M perpetual futures is derived from the associated underlying cryptocurrency, exemplified by the 0.0001 BTC face value for BTCUSDT.
- In Coin-M perpetual futures, the price of each contract is fixed in US dollars, as seen in the 100 USD face value for BTCUSD.
3. Different risks associated with the devaluation of collateral asset:
- In USDT-M perpetual futures, the collateral asset required is USDT. When the price of the underlying crypto falls, it does not affect the value of the USDT collateral asset.
- In Coin-M perpetual futures, the collateral asset required corresponds to the underlying crypto. When the price of the underlying crypto falls, the collateral assets required for the users’ positions increase, and more of the underlying crypto is needed as collateral.


